Brent continues to slip and WTI is along for the slide-ride too. Over the last two weeks, we’ve seen price floors getting lowered only to be breached again sooner than most expect. The Oilholic’s latest 5-day assessment saw both benchmarks as well as the OPEC basket of crudes end the week below US$90 per barrel on Friday.
One has been putting forward a short position argument on Brent since the summer to the readers of this blog and in columns for Forbes. As the tale goes, yours truly has pretty much got the call right, except for a few weeks over one month. Speculators, including but not limited to hedge funds, triumphed in June using the initial flare-up in Iraq as pretence for driving the futures price up. Market fundamentals were never going to support a price spike to $115, as was the case back then.
Those banking on backwardation were bound to get left holding barrels of paper crude on their books that they never needed in the first place for anything other than trading for profit. As the date of the paper contract got desperately close to where you might have to turn up with a tanker at the end of a pipeline, hedge funds that went long in June ended up collectively holding just shy of 600 million paper barrels on their books.
Smart, strategic buying by physical traders eyeing cargoes without firm buyers made contango set in hitting the hedge funds with massive losses. The week to July 15 then saw hedge funds and other speculators cut their long bets by around 25%, reducing their net long futures and options positions in Brent to 151,981 from 201,568 according to ICE.
Physical traders, had finally taught paper traders a long overdue lesson that you can’t cheat market fundamentals for very long. So it was a pleasure expanding upon the chain of thought and discuss other ‘crude’ matters with Nick 'the Moose' Batsford and his jolly colleagues at Tip TV, on October 6. Here’s a link to the conversation for good measure.
Those banking on backwardation were bound to get left holding barrels of paper crude on their books that they never needed in the first place for anything other than trading for profit. As the date of the paper contract got desperately close to where you might have to turn up with a tanker at the end of a pipeline, hedge funds that went long in June ended up collectively holding just shy of 600 million paper barrels on their books.
Smart, strategic buying by physical traders eyeing cargoes without firm buyers made contango set in hitting the hedge funds with massive losses. The week to July 15 then saw hedge funds and other speculators cut their long bets by around 25%, reducing their net long futures and options positions in Brent to 151,981 from 201,568 according to ICE.
Physical traders, had finally taught paper traders a long overdue lesson that you can’t cheat market fundamentals for very long. So it was a pleasure expanding upon the chain of thought and discuss other ‘crude’ matters with Nick 'the Moose' Batsford and his jolly colleagues at Tip TV, on October 6. Here’s a link to the conversation for good measure.
Overall dynamic hasn’t altered from May. To begin with, of the five major global oil importers – China, India, Japan, US and South Korea – importation by four of the aforementioned is relatively down, with India being the odd one out going the other way. Secondly, if an ongoing war in the Middle East is unable to perk-up the price, you know the macroeconomic climate remains dicey with the less said about OECD oil demand the better.
Thirdly, odd as it may seem, while Iraqi statehood is facing an existential threat, there has been limited (some say negligible) impact on the loading and shipment of Basra Light. This was the situation early on in July and pretty much remains the case early October. There is plenty of crude oil out there while buyers are holding back.
Now if anything else, hedge funds either side of the pond have wised up considerably since the July episode. Many of the biggest names in the industry are net-short and not net-long at present, though some unwisely betting on the ‘only way is long’ logic will never learn. Of course, Bloomberg thinks the story is going. One has always had a suspicion that the merry team of that most esteemed data and newswire service secretly love this blog. Contacts at SocGen, Interactive Brokers and a good few readers of ADVFN have suggested so too.
 Ever since the Oilholic quipped that hedge funds had been contangoed and went on to substantiate it on more than one occasion via broadcast or print, this humble blog has proved rather popular with ‘Bloomberg-ers’ (see right, a visit earlier this week). Now take this coincidental October 6 story, where Bloomberg claims "Tumbling Oil Prices Punish Hedge Funds Betting on Gains."
Ever since the Oilholic quipped that hedge funds had been contangoed and went on to substantiate it on more than one occasion via broadcast or print, this humble blog has proved rather popular with ‘Bloomberg-ers’ (see right, a visit earlier this week). Now take this coincidental October 6 story, where Bloomberg claims "Tumbling Oil Prices Punish Hedge Funds Betting on Gains."
Behind the bold headline, the story doesn’t tell us how many hedge funds took a hit or the aggregate number of paper barrels thought to be on their books. Without that key information, the story and its slant are actually a meaningless regurgitation of an old idea. Let’s face it – ideas are not copyrighted. Some hedge fund somewhere will always lose money on a trading call that went wrong, but what’s the big deal, what’s new and where’s the news in the Bloomberg story? Now what happened in July was a big deal.
The 4.1% jump in net-long positions as stated in the Bloomberg report, only for the Saudis to adjust their selling price and cause a further oil price decline, does not signify massive blanket losses for the wider hedge funds industry. Certainly, nothing on July’s loss scale has taken place over the last four weeks either for the WTI or Brent, whether we use ICE or CFTC data.
So here’s some advice Bloomberg if you really feel like probing the matter meaningfully. In the style of Mr. Wolf from Pulp Fiction, if the Oilholic “is curt here, it’s because time is a factor” when putting these things together, “so pretty please with sugar on top” -
So here’s some advice Bloomberg if you really feel like probing the matter meaningfully. In the style of Mr. Wolf from Pulp Fiction, if the Oilholic “is curt here, it’s because time is a factor” when putting these things together, “so pretty please with sugar on top” -
(a) Try picking up the phone to some physical traders of the crude stuff, as price aggregators do, in order to get anecdotal evidence and thoughts based on their internal solver models, not just those who pay way too much for expensive data terminals and have never felt or known what a barrel of crude oil looks like. It'll help you get some physical market context.
(b) Reconcile at least two months of CFTC or ICE data either side of the pond to get a sense of who is electronically holding what.
(c) Take the aggregated figure of barrels held at a loss/profit to previous month as applicable, be bold and put a round figure estimate on what hedge funds might well be holding to back up loss/profit slant.
Or (d) if you don’t have the tenacity to do any of the above, email the Oilholic, who doesn’t fix problems like Mr. Wolf, but doesn’t bite either. In the meantime of course, we can keep ourselves fully informed with news about Celine Dion’s whereabouts (see above left, click to enlarge), as Will Hedden of IG Group noted in a recent tweet – the kind of important market moving news that reminds us all how good an investment a Bloomberg terminal is! That’s all for the moment folks! Keep reading, keep it ‘crude’!
Or (d) if you don’t have the tenacity to do any of the above, email the Oilholic, who doesn’t fix problems like Mr. Wolf, but doesn’t bite either. In the meantime of course, we can keep ourselves fully informed with news about Celine Dion’s whereabouts (see above left, click to enlarge), as Will Hedden of IG Group noted in a recent tweet – the kind of important market moving news that reminds us all how good an investment a Bloomberg terminal is! That’s all for the moment folks! Keep reading, keep it ‘crude’!
To follow The Oilholic on Twitter click here.
To follow The Oilholic on Google+ click here.
To follow The Oilholic on Forbes click here.
To email: gaurav.sharma@oilholicssynonymous.com
To follow The Oilholic on Google+ click here.
To follow The Oilholic on Forbes click here.
To email: gaurav.sharma@oilholicssynonymous.com
© Gaurav Sharma 2014. Photo 1: Shell Oil Rig, USA © Shell. Photo 2: Bloomberg's visit to the Oilholic, Oct 6, 2014 © Gaurav Sharma. Photo 3: Bloomberg Terminal with Celine Dion flashes © Will Hedden, IG Group, August 2014.









.jpg)




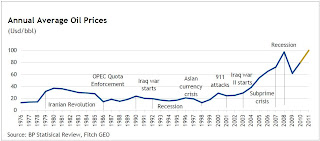 It has been a month of quite a few interesting reports and comments, but first and as usual - a word on pricing. Both Brent crude oil and WTI futures have partially retreated from the highs seen last month, especially in case of the latter. That’s despite the Libyan situation showing no signs of a resolution and its oil minister Shukri Ghanem either having defected or running a secret mission for Col. Gaddafi depending on which news source you rely on! (Graph 1: Historical average annual oil prices. Click on graph to enlarge.)
It has been a month of quite a few interesting reports and comments, but first and as usual - a word on pricing. Both Brent crude oil and WTI futures have partially retreated from the highs seen last month, especially in case of the latter. That’s despite the Libyan situation showing no signs of a resolution and its oil minister Shukri Ghanem either having defected or running a secret mission for Col. Gaddafi depending on which news source you rely on! (Graph 1: Historical average annual oil prices. Click on graph to enlarge.)