It has been a crudely British fortnight in terms of Black Gold related news, none more so than BP’s announcement – on March 3 – that it has reached a settlement of US$7.8 billion with the Plaintiffs' Steering Committee (PSC) for civil charges related to the 201 Macondo oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico.
The settlement amount is at the upper end of market conjecture and certainly well above conservative estimates. However, it does not mean that the US government is going to in any way, shape or form, let up on BP – especially in an election year. Everyone knows that, especially BP. However for a second time, the trial case brought against it will have to be delayed as the US Judge in the case – Carl Barbier – noted the settlement would lead to a “realignment of the parties in this litigation and require substantial changes to the current Phase I trial plan, and in order to allow the parties to reassess their respective positions.”
The settlement amount is at the upper end of market conjecture and certainly well above conservative estimates. However, it does not mean that the US government is going to in any way, shape or form, let up on BP – especially in an election year. Everyone knows that, especially BP. However for a second time, the trial case brought against it will have to be delayed as the US Judge in the case – Carl Barbier – noted the settlement would lead to a “realignment of the parties in this litigation and require substantial changes to the current Phase I trial plan, and in order to allow the parties to reassess their respective positions.”
The US government maintains that the US$7.8 billion deal does not address "significant damages" to the environment but PSC-BP agreement is expected to benefit regional 100,000 fishermen, local residents and clean-up workers who suffered following the spill.
BP says it expects the money to come from a US$20 billion compensation fund it had previously set aside and the response of the wider market and ratings agencies to the settlement has been positive. While reaffirming BP’s long term Issuer Default Rating (IDR) at ‘A’, Fitch Ratings notes that BP has adequate financial resources to meet its remaining oil spill related obligations currently estimated by the agency at US$20 billion between 2012 and 2014.
This figure includes the remainder of BP's provisioned costs of US$10.6 billion and approximately US$10 billion of Fitch assumed additional litigation related payments, excluding potential fines for gross negligence. As of end-December 2011, BP had adequate financial resources to meet this obligation with US$14.1 billion of ‘on balance sheet’ cash and US$6.9 billion of undrawn committed stand-by and revolving credit lines. Additionally, the company plans to dispose of assets for about US$18 billion by end-2013 within its US$38 billion asset disposal programme.
Fitch Ratings estimates BP's total Gulf of Mexico spill related payments, net of partner recoveries, will range between US$45 billion and US$50 billion assuming BP was not grossly negligent. BP's cash outflow related to the Gulf of Mexico oil spill amounted to US$26.6 billion by end-2011, net of partner recoveries.
S&P also views the settlement as “somewhat supportive” for its ‘A/A-1/Stable’ ratings on BP and consistent with the agency’s base-case assumptions. “This is because the settlement addresses some material litigation and payment uncertainties, and because we understand that the plaintiffs cannot pursue further punitive damages against BP as a condition of the settlement,” it says.
BP has not admitted liability and still faces other legal claims at State and Federal level. Nonetheless, while the settlement is credit supportive, market commentators in City feel the uncertainty related to the total oil spill liability is not ending any time soon. The Oilholic feels an investigation by US Department of Justice against BP into the oil spill incident encompassing possible violations of US civil or criminal laws could be a potential banana skin as no love has been lost between the two. With several cases still ongoing, a settlement with PSC was a first of many legal hurdles for BP; albeit an important one.
Away from the legal wrangles of “British Petroleum” as US politicians love to call it, Brits themselves had to contend with a record high price of petrol at the pump this week – an average gas station forecourt quote of 137.3 pence per litre on March 5, according to the UK Department of Energy and Climate Change (DECC). The previous record of 137.05p was set on May 9, 2011. However, private research by Experian Catalist says the high is a little “higher” at 137.44p per litre.
And if you thought, the Oilholic’s diesel-powered readership was faring any better, the diesel price is hit a record high of 144.7p per litre, up 0.8p from the previous UK record, which was set the week before! As if that wasn’t enough – the country’s (Markit/CIPS) Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) for manufacturing slipped to 51.2 in February, down from 52 in January with analysts blaming the high cost oil for manufacturers which rose at the fastest rate in 19 years. It presents another serious quandary for UK Chancellor George Osborne who’s due to table his government’s Union budget on March 21st.
From the price of the refined stuff at British gas station forecourts to the price of a barrel of the crude stuff on the futures market – which saw Brent resisting the US$125 level and WTI resisting the US$106 level for the forward month contract. Myrto Sokou, analyst at Sucden Financial, reckons stronger US economic data brought back risk appetite and improved sentiment this week.
Greece is going to be a main focus for the market with hopes of a positive result on its debt bailout, Sokou adds, but amid renewed rumours whether it would be better for the country to leave the Euro. Cautious optimism is ‘crudely’ warranted indeed.
Elsewhere, the Indian government's attempt divest a 5% stake in one of its NOCs – the Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) – via public share offering fell marginally short of expectations last week. Despite tall claims of oversubscription, only 98% of the shares on sale were subscribed. With high hopes of raising something in the region of US$2.5 billion, the government had offered 428 million shares at a price of INR290 per share (approximately US$5.85 and 2% higher than ONGC average share price for February).
However, the Oilholic thinks that even for a company which admittedly has a massive role in a burgeoning domestic market, the price offer was strange at best and overpriced at worst. This probably put off many of the country’s average middle tier investors, especially as many used February’s price as a reference point. Who can blame them and perhaps the Indian government is wiser for the experience too. That’s all for the moment folks. Keep reading, keep it ‘crude’!
© Gaurav Sharma 2012. Photo: Aerial of the Helix Q4000 taken shortly before "Static Kill" procedure began at Macondo (MC 252) site in Gulf of Mexico, August 3, 2010 © BP Plc.





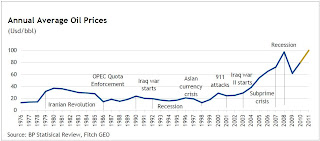 It has been a month of quite a few interesting reports and comments, but first and as usual - a word on pricing. Both Brent crude oil and WTI futures have partially retreated from the highs seen last month, especially in case of the latter. That’s despite the Libyan situation showing no signs of a resolution and its oil minister Shukri Ghanem either having defected or running a secret mission for Col. Gaddafi depending on which news source you rely on! (Graph 1: Historical average annual oil prices. Click on graph to enlarge.)
It has been a month of quite a few interesting reports and comments, but first and as usual - a word on pricing. Both Brent crude oil and WTI futures have partially retreated from the highs seen last month, especially in case of the latter. That’s despite the Libyan situation showing no signs of a resolution and its oil minister Shukri Ghanem either having defected or running a secret mission for Col. Gaddafi depending on which news source you rely on! (Graph 1: Historical average annual oil prices. Click on graph to enlarge.)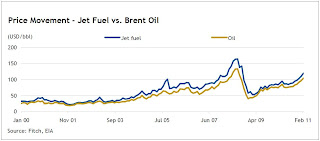



 The evidence is clear, integrated oil companies have and will continue to divest in downstream assets particularly refineries because upstream investment culture of high risk, high rewards trumps it.
The evidence is clear, integrated oil companies have and will continue to divest in downstream assets particularly refineries because upstream investment culture of high risk, high rewards trumps it.