 In 1999, the merger of Exxon and Mobil created what could be described as an oil & gas industry behemoth and, using some financial metrics, perhaps also one of the most profitable among the international “supermajors”. Despite being a global entity, for many people ExxonMobil remains an enigma.
In 1999, the merger of Exxon and Mobil created what could be described as an oil & gas industry behemoth and, using some financial metrics, perhaps also one of the most profitable among the international “supermajors”. Despite being a global entity, for many people ExxonMobil remains an enigma.
Its sheer presence on the world stage has its admirers yet critics have labelled it as a polluter, a climate-change denier, a controversial lobbyist, a bully and more. For Pulitzer Prize winning author Steve Coll, there is more to it than meets the eye when it comes to ExxonMobil and its financial performance which is more durable than others in the Fortune 500 list.
Minus generalisations or a linear exercise in big oil bashing, this latest work of Coll's – Private Empire: ExxonMobil and American Power – is a pragmatic book about a global brand which, in the author’s words, became the "most hated" oil company in America after the Exxon Valdez oil spill off the coast of Alaska in 1989.
That incident itself provides the starting point for a detailed narrative of just under 700 pages, split into two parts – The End of Easy Oil and The Risk Cycle – containing 28 chapters. Banking on his journalistic tenacity and detailed research work including over 400 interviews, declassified documents, legal and corporate records and much more, Coll has pencilled his unique description of this “Private Empire” and it does not disappoint.
ExxonMobil has its dogmas, fears, idiosyncrasies, pluses and minuses and the author delves into these based on anecdotal as well as observed evidence. From an obsession with safety post Exxon Valdez to the moving of its headquarters to Irving, Texas, from “the merger” to an insistence on R.O.C.E (Return on Capital Employed) – Coll has tackled it all.
The author opines that far from being an attention seeking ruthless corporate giant in bed with politicians, as popular conjecture would have you believe, ExxonMobil’s legendary lobbying in Washington DC was cleverly and aggressively targeted for maximum effect. While it shunned overt politicising of its presence and affairs, the company benefitted from new markets and global commerce that US military hegemony protected the world over. After all, when fighting a tight corner, ExxonMobil often called in a favour from power brokers on Capitol Hill.
While the whole book is a thoroughly good read, for the Oilholic, reading Coll’s description of ExxonMobil’s grapples with "resource nationalism" in developing markets (as its oil output in developed jurisdictions started declining) and its management (or otherwise) of operations in inhospitable countries, were the two most interesting passages.
From Aceh in Indonesia to the Niger Delta, from the Gulf of Guinea to Chad, ExxonMobil found itself in alien territory and conflicts it had not seen before. But it strategized, adopted, called in favours and more often than not emerged with a result in its favour; if not immediately, then over a period of time, writes Coll.
Every saga needs a cast of characters and this one is no exception. One individual and his portrayal by the author stand out. That’s Lee ("Iron Ass") Raymond, ExxonMobil’s inimitable boss from 1993 to 2005. With a doctorate in chemical engineering, boasting Dick Cheney among his friends and a history of denying climate change, Raymond was by all accounts a formidable character and Coll’s description of him does not disappoint. One mute criticism the Oilholic has is that its borderline gossip in parts but one supposes the gossip joins the dots in a weighty narrative.
In summation, this blogger found the book to be a definitive one on ExxonMobil and by default a glimpse into the wider ‘crude’ world, it’s wheeling and dealing. The Oilholic would be happy to recommend it to anyone interested in the oil business, its history, market dynamics and the geopolitical climate it is inextricably linked with.
Those interested in business, finance and economics would also enjoy this book as would the mainstream non-fiction reader in search of a riveting real world account. Finally, it would also be well worth the while of students of financial journalism to read and learn from Coll’s craft.
© Gaurav Sharma 2012. Photo: Front Cover – Private Empire: ExxonMobil and American Power © Allen Lane / Penguin Group UK.
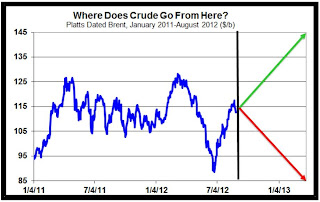
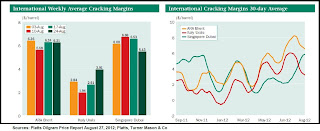


.jpg)





